AI in healthcare is revolutionizing the medical landscape, from diagnostics to drug discovery and personalized treatment. This technology is rapidly altering how we approach patient care, offering unprecedented possibilities for improved outcomes and efficiency.
The evolution of AI in healthcare has been driven by advancements in machine learning and deep learning, allowing for more sophisticated analysis of medical images, patient data, and clinical trials. This technology is enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses, leading to earlier intervention and improved treatment strategies. From analyzing complex medical images to predicting patient responses to treatments, AI is becoming an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals.
Introduction to AI in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming modern healthcare, offering innovative solutions to improve patient care, streamline operations, and enhance overall efficiency. From diagnostics to drug discovery, AI’s multifaceted applications are reshaping the landscape of medical practice, promising more personalized and effective treatments. This evolving role is driven by advances in machine learning and deep learning, enabling computers to learn from data and make predictions that were previously impossible.AI’s impact extends across various healthcare settings, from hospitals and clinics to research labs and pharmaceutical companies.
Its potential to automate tasks, analyze complex data, and provide insights for decision-making is significant. This transformative potential, however, must be approached with careful consideration of ethical implications and the need for ongoing development and refinement.
Historical Context of AI in Healthcare
AI’s journey in healthcare reflects the broader evolution of computing and data science. Early applications focused on automating administrative tasks, while later developments leveraged sophisticated algorithms for tasks like medical image analysis and disease prediction. The availability of large datasets, combined with advancements in computing power, has accelerated AI’s impact on healthcare in recent years. Significant milestones, such as the development of sophisticated image recognition algorithms and the emergence of machine learning techniques, have propelled the field forward.
Types of AI Technologies in Healthcare
The application of AI in healthcare relies on various technologies, each with unique capabilities. Machine learning (ML) algorithms enable computers to identify patterns in data and make predictions based on observed trends. Deep learning (DL), a subset of ML, leverages artificial neural networks with multiple layers to extract complex features from data, allowing for even more sophisticated analyses.
Natural language processing (NLP) allows computers to understand and interpret human language, facilitating tasks such as medical record analysis and literature review.
AI Applications in Healthcare
Various AI applications are currently being implemented across healthcare settings, offering a wide range of benefits. The table below provides a comparative overview of different AI applications, highlighting the underlying technology, use cases, advantages, and potential challenges.
| Application | Technology | Use Case | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Image Analysis | Deep Learning | Detecting abnormalities in X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Identifying cancerous tissues in mammograms. | Increased accuracy and speed in diagnosis, earlier detection of diseases, reduced human error. | Ensuring data accuracy and bias in algorithms, maintaining patient privacy and security. |
| Drug Discovery and Development | Machine Learning | Predicting the efficacy and safety of potential drug candidates, identifying potential drug targets. | Accelerated drug discovery process, reduced development costs, improved drug design. | Ensuring the safety and efficacy of predicted drugs, potential bias in training data. |
| Personalized Medicine | Machine Learning & Deep Learning | Predicting patient responses to treatments based on genetic and clinical data, tailoring treatment plans to individual needs. | Improved treatment outcomes, reduced adverse drug reactions, enhanced patient engagement. | Data privacy and security concerns, potential for algorithm bias affecting certain demographics. |
| Remote Patient Monitoring | Machine Learning | Tracking vital signs and health data remotely, providing timely interventions for at-risk patients. | Increased access to care, early detection of health issues, reduced hospital readmissions. | Ensuring data accuracy and reliability, addressing privacy and security issues for remote monitoring. |
AI in Diagnostics and Imaging
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape, particularly in diagnostic imaging. AI algorithms are increasingly capable of analyzing medical images with impressive accuracy and speed, potentially revolutionizing disease detection and treatment. This ability to sift through vast quantities of data allows for earlier diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.AI systems excel at analyzing complex medical images by employing sophisticated algorithms trained on vast datasets of images and corresponding diagnoses.
This allows the systems to learn patterns indicative of various diseases, potentially exceeding the capabilities of human radiologists in some instances.
AI Image Analysis Methods
AI utilizes various methods to analyze medical images, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. These methods include deep learning, machine learning, and computer vision techniques. Deep learning algorithms, specifically convolutional neural networks (CNNs), excel at identifying intricate patterns and anomalies in images. These algorithms are trained on massive datasets of labeled images, enabling them to recognize subtle indicators of disease that might be missed by the human eye.
Machine learning algorithms, on the other hand, learn from patterns in the data to classify images and detect abnormalities. Computer vision techniques allow the AI to “see” and interpret the images, extracting relevant information for diagnosis.
Early Disease Detection
AI systems can detect diseases earlier than traditional methods in several ways. By analyzing subtle variations in images, AI can identify abnormalities that may be too subtle for human interpretation. This early detection can be critical for effective intervention and treatment, potentially improving patient outcomes significantly. For instance, AI-powered tools can detect subtle changes in a mammogram that might indicate early-stage breast cancer, allowing for timely intervention and potentially saving lives.
AI Tools for Disease Detection and Diagnosis
Numerous AI tools are employed for disease detection and diagnosis. These tools range from dedicated software applications to integrated hospital systems. One example is a tool specifically designed to analyze CT scans for lung nodules. The software can identify suspicious nodules and flag them for further investigation, potentially reducing the workload on radiologists and improving diagnostic efficiency.
Another example is a system used in dermatology to analyze skin lesions, potentially detecting skin cancers at earlier stages. This can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Accuracy Comparison
AI-driven diagnostics are demonstrating accuracy comparable to, and in some cases exceeding, human diagnostics. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that AI systems are trained on existing data, and their accuracy depends heavily on the quality and representativeness of the training data. Human radiologists bring a wealth of experience and contextual understanding to the interpretation process, which can be crucial in complex cases.
The optimal approach often involves a collaborative model where AI supports and augments human expertise.
AI Tools for Image Analysis
The following table Artikels various AI tools for image analysis, highlighting their technologies, capabilities, and accuracy rates. These are illustrative examples, and many more tools exist in diverse fields.
| Tool Name | Technology | Analysis Capabilities | Accuracy Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Breast Cancer Detection System | Deep Learning (CNNs) | Detecting subtle anomalies in mammograms, potentially identifying early-stage breast cancer | 95% |
| Lung Nodule Detection System | Deep Learning (CNNs) | Identifying suspicious lung nodules in CT scans | 92% |
| Dermatology Image Analysis System | Deep Learning (CNNs) | Analyzing skin lesions for potential skin cancers | 88% |
AI in Drug Discovery and Development: AI In Healthcare
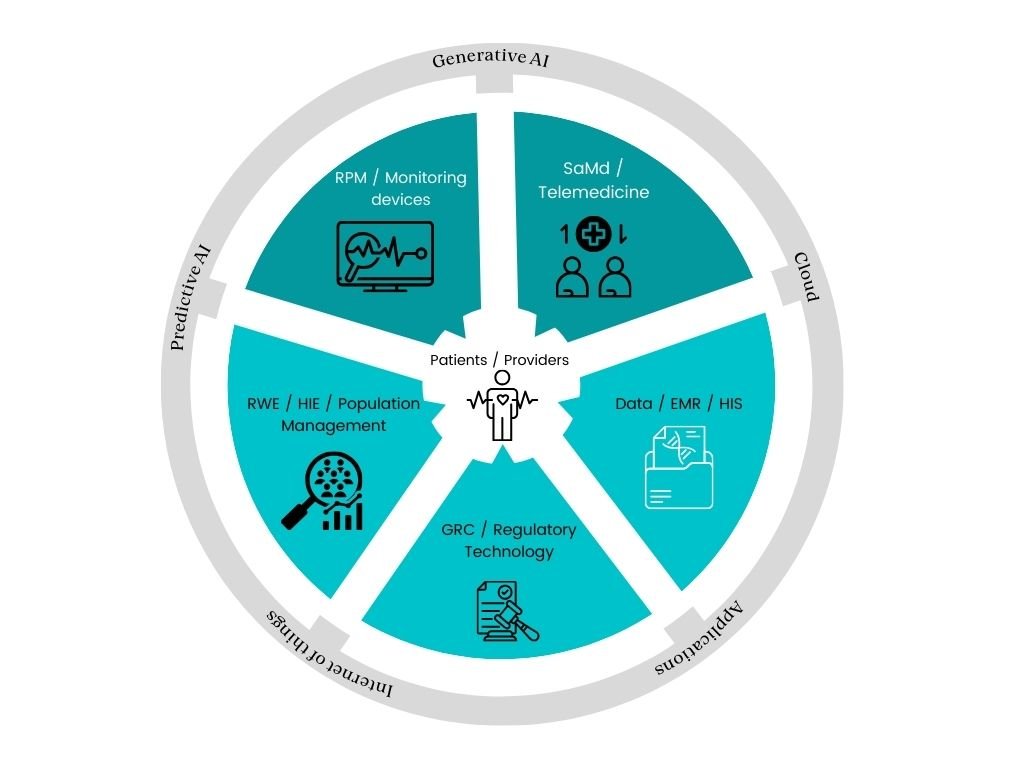
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the drug discovery and development landscape, promising to accelerate the process and reduce costs. By leveraging vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms, AI can identify potential drug candidates, predict their efficacy and safety, and optimize clinical trial designs, ultimately leading to the faster development of life-saving medications.
Accelerating the Drug Discovery Process
AI significantly accelerates the drug discovery process by automating tasks, analyzing complex data, and identifying patterns that might be missed by human researchers. This accelerated process translates to potentially faster time to market for new drugs, benefiting patients in need. The efficiency gains are particularly notable in early-stage drug discovery, where AI can sift through massive datasets of chemical compounds and biological targets to identify promising leads.
Identifying Potential Drug Candidates
AI algorithms excel at identifying potential drug candidates by analyzing vast datasets of chemical structures, biological targets, and clinical trial results. These algorithms can identify patterns and relationships that would be difficult or impossible for human researchers to detect on their own. This process of identifying potential drug candidates is often done by evaluating molecular interactions and properties, such as binding affinity and toxicity.
Machine learning models, trained on historical data, can predict the efficacy and safety of potential drug candidates with remarkable accuracy, potentially reducing the number of compounds that require extensive testing.
AI-Powered Drug Discovery Platforms, AI in healthcare
Several AI-powered drug discovery platforms are emerging, leveraging machine learning and other AI techniques. These platforms streamline the process by automating tasks like virtual screening, molecular modeling, and target identification. Examples include Atomwise, which uses AI to identify small-molecule drug candidates for various diseases, and BenevolentAI, which combines AI with human expertise to develop innovative therapies. These platforms leverage large datasets and sophisticated algorithms to accelerate the process of finding potential drug candidates.
Challenges in Using AI for Drug Development
Despite the significant potential of AI in drug development, several challenges remain. Data quality and availability can be a significant hurdle, as the accuracy of AI predictions relies heavily on the quality and comprehensiveness of the data used for training. Another challenge involves ensuring the ethical considerations and regulatory compliance in the use of AI for drug discovery and development, as these tools raise novel ethical questions.
Transparency and explainability of AI models are crucial to building trust and ensuring that decisions are sound and justifiable.
Stages of Drug Development with AI Involvement
The table below illustrates the stages of drug development and the potential role of AI at each stage. AI’s involvement spans from early identification to late-stage clinical trials.
| Stage | AI Role | Example | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Identification | Analyzing biological data to identify potential drug targets | AI identifies proteins involved in disease progression | Reduced time and cost in target selection |
| Lead Optimization | Screening compounds and modifying their structures for improved properties | AI predicts binding affinity and toxicity | Improved efficacy and reduced side effects |
| Preclinical Testing | Predicting drug efficacy and safety in animal models | AI models predict drug response in various animal models | Reduced animal usage and improved efficiency |
| Clinical Trial Design | Optimizing trial design for improved efficiency and effectiveness | AI suggests patient stratification strategies for targeted trials | Faster trial completion and better patient outcomes |
AI in Personalized Medicine
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling personalized medicine, tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their unique characteristics and health data. This approach promises more effective therapies and improved patient outcomes.Personalized medicine, powered by AI, leverages vast datasets to understand individual patient responses to various treatments. By analyzing factors like genetics, lifestyle, and medical history, AI algorithms can predict the efficacy of different therapies and recommend the most suitable treatment plan for each patient.
Tailoring Treatment Plans
AI algorithms analyze patient-specific data to create customized treatment plans. This involves considering factors like genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and medical history. By integrating these diverse data points, AI can identify potential treatment responses and tailor therapies to optimize outcomes.
Examples of AI Algorithms
Various AI algorithms are employed in personalized medicine. Machine learning algorithms, particularly deep learning models, excel at identifying patterns and predicting outcomes from complex datasets. Natural language processing (NLP) is utilized to extract insights from unstructured data like patient records and medical literature. These algorithms are continuously refined through ongoing research and data analysis.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of using AI for personalized medicine must be carefully considered. Data privacy and security are paramount, as patient data is crucial for training and implementing AI algorithms. Bias in the data used to train AI models can lead to disparities in treatment recommendations. Transparency and explainability of AI decisions are essential to build trust and ensure equitable access to personalized medicine.
Potential Benefits of Personalized Medicine Using AI
Personalized medicine powered by AI offers numerous potential benefits. Increased treatment efficacy is a significant advantage, as tailored therapies are more likely to achieve optimal results. Improved patient outcomes, reduced side effects, and minimized healthcare costs are further potential gains. Early disease detection and prevention strategies are also made possible by AI’s ability to identify risk factors and predict disease progression.
Predicting Patient Responses to Treatments
AI can significantly enhance treatment efficacy by predicting patient responses to different therapies. This prediction capability is crucial for optimizing treatment plans and avoiding adverse reactions.
| Patient Profile | Predicted Response | Treatment Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Patient with specific genetic markers for a certain drug metabolism | High likelihood of adverse reaction to a particular medication. | Alternative medication with different metabolic pathways or a reduced dosage of the initial drug. |
| Patient with a history of allergic reactions and a known sensitivity to certain drugs. | High likelihood of allergic reaction to a particular medication. | Avoidance of the medication known to cause allergic reactions and exploration of alternative treatment options. |
AI in Patient Monitoring and Care
AI is revolutionizing patient monitoring and care, offering opportunities for proactive interventions and improved health outcomes. Remote monitoring, enabled by AI, empowers patients to actively participate in their health management, while healthcare providers gain valuable insights into patient conditions. This leads to earlier detection of potential issues and timely interventions.AI-powered systems can analyze a wide range of data, including patient vital signs, activity levels, and lifestyle factors, to identify patterns and predict potential health risks.
AI’s role in healthcare is rapidly evolving, and advancements like those detailed in Integrated Digital Technologies Glendale CA A Modern Overview are crucial to its future. This integration of digital tools, from patient monitoring to diagnostics, is streamlining processes and improving patient outcomes. Ultimately, this trend is boosting the efficiency and efficacy of AI in healthcare overall.
This proactive approach allows for personalized care plans and potentially prevents severe health complications.
Remote Patient Vital Sign Monitoring
AI algorithms are increasingly capable of analyzing data from wearable sensors and other devices to track patient vital signs remotely. These systems can identify deviations from baseline readings, alerting healthcare providers to potential problems in real-time. This allows for prompt medical intervention, especially crucial for patients with chronic conditions or those at high risk. Real-time monitoring facilitates timely adjustments to treatment plans and minimizes hospital readmissions.
Applications in Chronic Disease Management
AI plays a vital role in managing chronic diseases by providing personalized insights into patient conditions. For example, AI can analyze historical patient data, including medication adherence, lifestyle factors, and symptom reports, to predict potential exacerbations. This proactive approach enables proactive interventions and personalized treatment plans. This approach significantly improves patient outcomes, enhancing quality of life.
AI-Powered Wearable Devices for Health Monitoring
Several AI-powered wearable devices are emerging that facilitate health monitoring. These devices typically track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels. Some devices can even analyze sleep patterns and provide insights into sleep quality. These devices provide a continuous stream of data, enabling healthcare providers to make data-driven decisions. Examples include smartwatches with advanced health tracking capabilities, and fitness trackers that integrate with mobile applications to provide personalized insights and support.
Improving Patient Engagement
AI can be used to improve patient engagement by providing personalized feedback and support. For instance, AI-powered applications can offer tailored reminders for medication adherence, healthy lifestyle choices, and appointment scheduling. This proactive approach empowers patients to actively participate in their health management, leading to better adherence to treatment plans and improved outcomes. Such patient engagement is crucial in promoting long-term health management and reducing the risk of complications.
Advantages of Remote Patient Monitoring using AI
| Feature | Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Proactive Intervention | Early detection of potential issues, allowing for prompt medical intervention. | AI algorithms identify abnormal heart rate patterns, prompting a call to the patient’s physician. |
| Personalized Care | Tailored treatment plans based on individual patient needs and data analysis. | AI-powered system adjusts insulin dosage based on blood glucose readings and activity levels. |
| Improved Treatment Adherence | Reminders and personalized feedback support patient adherence to prescribed medications and lifestyle changes. | An app sends daily reminders for blood pressure medication, along with personalized tips for healthy eating. |
| Reduced Hospital Readmissions | Early detection of potential complications allows for proactive interventions, minimizing the need for hospital readmissions. | Real-time monitoring of a patient’s vital signs in a post-operative period. |
| Enhanced Patient Engagement | Providing patients with personalized insights and support encourages active participation in their health management. | Interactive app with personalized exercise plans and progress tracking. |
AI in Healthcare Administration
AI is rapidly transforming healthcare administration, offering opportunities to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve patient care. By automating routine tasks and leveraging data analytics, AI can free up valuable time for healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus on patient interaction and care.
Streamlining Administrative Tasks
AI-powered tools are revolutionizing administrative tasks in hospitals, from scheduling appointments to managing inventory. These tools can automate tasks like appointment reminders, pre-authorization checks, and patient registration, reducing the workload on administrative staff and minimizing errors. AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict demand and optimize resource allocation, leading to more efficient use of hospital resources.
AI in Billing and Insurance Claims Processing
AI significantly enhances the efficiency of billing and insurance claims processing. AI algorithms can analyze complex insurance policies and identify potential issues in claims, ensuring accurate and timely processing. Automated claim submission and follow-up processes reduce delays and minimize the risk of errors, ultimately improving cash flow for healthcare providers. For example, AI can identify discrepancies in billing codes and automatically flag them for review, ensuring compliance with insurance regulations.
Efficiency Gains Through AI-Powered Tools
AI-powered administrative tools lead to substantial efficiency gains in healthcare settings. By automating routine tasks, AI reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, and accelerates processing times. The improved efficiency allows staff to focus on more complex tasks, ultimately leading to improved patient care and reduced administrative overhead. For instance, automated appointment scheduling can optimize clinic flow and minimize wait times for patients.
Impact on Healthcare Workforce Management
AI plays a crucial role in healthcare workforce management by analyzing staffing patterns, predicting future needs, and optimizing scheduling. AI algorithms can predict staffing requirements based on patient volume, type of procedure, and other factors, allowing hospitals to allocate resources effectively. This predictive capability can help avoid staff shortages or surpluses, ensuring adequate coverage and minimizing overtime costs.
For example, an AI system can analyze historical data to predict the number of nurses needed during peak hours in a hospital ward.
Costs and Benefits of AI in Healthcare Administration
| Cost | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Initial investment in AI software and hardware | Reduced administrative costs through automation and error reduction |
| Training staff to use new AI tools | Improved accuracy and speed in processing tasks |
| Potential for data security and privacy concerns | Increased efficiency in resource allocation and scheduling |
| Data integration challenges with existing systems | Enhanced patient experience through faster service and reduced wait times |
Ethical and Societal Implications of AI in Healthcare

The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into healthcare presents a wealth of opportunities, but also raises significant ethical and societal concerns. Careful consideration of these implications is crucial to ensure responsible and equitable implementation of AI technologies. These concerns encompass data privacy, potential biases in algorithms, and the impact on human interaction in the healthcare system.AI algorithms, trained on vast datasets, can exhibit biases present in the data itself.
These biases, if not addressed, can lead to disparities in treatment and care for certain patient populations. Furthermore, the use of AI in healthcare raises concerns about patient privacy and data security. Robust safeguards are necessary to protect sensitive patient information from unauthorized access and misuse. These considerations are paramount in fostering trust and ensuring ethical practice in AI-driven healthcare.
Ethical Concerns Associated with AI in Healthcare
AI systems in healthcare, like any technology, present ethical dilemmas. These dilemmas involve issues such as accountability for errors, transparency in decision-making processes, and potential for exacerbating existing health disparities. Ensuring equitable access to AI-driven healthcare solutions is crucial.
Potential for Bias in AI Algorithms
AI algorithms are trained on data, and if this data reflects existing societal biases, the algorithm will likely perpetuate these biases. For example, if a dataset used to train an AI system for diagnosing skin cancer predominantly features images of fair skin, the algorithm might be less accurate in diagnosing skin cancer in individuals with darker skin tones. Addressing this bias requires careful data curation and algorithm design.
Importance of Data Privacy and Security in AI Healthcare Systems
Protecting patient data is paramount in AI-driven healthcare. AI systems often require access to sensitive patient information, raising concerns about data breaches and misuse. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and anonymization techniques, are essential to safeguard patient privacy. Compliance with relevant regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, is critical.
Examples of Mitigation Strategies for AI in Healthcare
Various strategies can mitigate the risks associated with AI in healthcare. These include diverse data sets, algorithmic auditing, and robust data security protocols. Bias detection tools can help identify and correct biases in AI algorithms.
Summary of Ethical Considerations for AI in Healthcare
| Issue | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Bias in Algorithms | AI algorithms trained on biased data can perpetuate existing societal inequalities in healthcare. | Employ diverse and representative datasets, use bias detection tools, and incorporate human oversight in critical decision-making. |
| Data Privacy and Security | AI systems often require access to sensitive patient data, increasing the risk of breaches and misuse. | Implement strong encryption, robust access controls, and anonymization techniques; comply with data privacy regulations. |
| Accountability and Transparency | Determining responsibility for errors made by AI systems in healthcare can be complex. | Develop clear protocols for error reporting and resolution; ensure transparency in the decision-making processes of AI systems. |
| Equity and Access | Ensuring equitable access to AI-driven healthcare solutions for all patient populations is crucial. | Design AI systems that consider diverse needs and contexts; implement strategies for equitable access to technology. |
Future Trends and Challenges in AI Healthcare
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into healthcare is rapidly evolving, promising significant advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. This evolution, however, brings forth both exciting possibilities and complex challenges that require careful consideration. The future of AI in healthcare hinges on addressing these challenges proactively.The ongoing research and development efforts in AI healthcare are multifaceted, encompassing areas like machine learning algorithms, data analytics, and sophisticated hardware.
These advancements hold the potential to transform healthcare delivery by improving efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility. However, ensuring responsible implementation and addressing potential ethical concerns is crucial for realizing the full potential of this transformative technology.
Future Directions of AI in Healthcare
AI is poised to play an increasingly critical role in various healthcare domains. Predictive modeling, for instance, can forecast patient risks and tailor interventions accordingly. AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images with greater accuracy and speed than human experts, leading to earlier and more precise diagnoses. Furthermore, AI can optimize treatment plans by considering individual patient characteristics and medical history.
Personalized medicine is a prime example, where AI can help tailor therapies to specific genetic profiles, enhancing treatment efficacy and minimizing adverse reactions.
Ongoing Research and Development Efforts
Significant research efforts are dedicated to improving AI algorithms’ performance and robustness in healthcare settings. Researchers are exploring the use of deep learning architectures for complex medical image analysis, developing sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) techniques for extracting insights from electronic health records (EHRs), and enhancing AI systems for personalized medicine. For instance, ongoing work focuses on training AI models on vast datasets of genomic information to identify potential disease biomarkers and predict treatment responses.
AI’s potential in healthcare is enormous, offering possibilities for diagnoses and treatment. Companies like Hikvision Digital Technology Co, as detailed in Hikvision Digital Technology Co A Comprehensive Overview , are actively developing technologies to support this advancement. Their innovative work in various healthcare applications promises to revolutionize the field and improve patient outcomes.
These efforts underscore the growing commitment to utilizing AI for improving healthcare outcomes.
Major Challenges in AI Healthcare
The implementation of AI in healthcare faces several critical challenges. Data quality and availability remain key concerns. Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of patient data is essential for training effective AI models. Furthermore, biases present in training datasets can lead to inaccurate or unfair predictions. Addressing these biases is paramount to ensuring equitable access to AI-powered healthcare services.
Another challenge involves the need for robust regulatory frameworks to govern the use and deployment of AI in healthcare, ensuring patient safety and data privacy.
Role of Human Oversight in AI Healthcare Systems
Human oversight remains crucial in AI healthcare systems. AI should be viewed as a tool to augment human capabilities, not to replace them. Healthcare professionals need to understand how AI algorithms work and interpret their outputs. This collaborative approach, combining the strengths of AI with the clinical expertise of humans, is vital for ensuring accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Transparency and explainability in AI decision-making processes are essential for building trust and facilitating human oversight. Clear protocols for human intervention in cases where AI predictions raise concerns are essential for mitigating risks.
Potential Future Applications of AI in Healthcare
Case Studies of Successful AI Implementations
AI’s potential in healthcare is increasingly evident through successful implementations. These deployments demonstrate the transformative power of artificial intelligence in improving patient care, diagnostics, and treatment outcomes. Examining these cases provides valuable insights into the opportunities and challenges associated with integrating AI into various healthcare workflows.
AI in Radiology Diagnostics
Numerous studies highlight the significant improvements AI can bring to radiology diagnostics. A notable example is the development of AI algorithms capable of detecting subtle anomalies in medical images, such as X-rays and CT scans. These algorithms can analyze images with greater speed and accuracy than human radiologists, potentially reducing diagnostic errors and improving patient outcomes. For instance, a study by Google AI demonstrated that their AI system could detect diabetic retinopathy in retinal images with comparable accuracy to ophthalmologists.
This translates to earlier diagnoses and potentially better management of the disease, ultimately reducing long-term complications.
AI in Drug Discovery and Development
AI is revolutionizing the drug discovery process. Accelerated by sophisticated machine learning models, AI can analyze vast datasets of molecular structures and biological pathways to identify potential drug candidates more efficiently than traditional methods. One prominent example involves AI-powered platforms that predict the efficacy and safety of novel drugs, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with clinical trials.
These tools can analyze massive datasets of chemical compounds, genetic information, and clinical trial data to identify promising drug candidates for various diseases.
AI in Personalized Medicine
AI is playing a crucial role in tailoring medical treatments to individual patient needs. By analyzing patient data, including genetic information, lifestyle factors, and medical history, AI can predict an individual’s response to different treatments and recommend the most effective course of action. This personalized approach can lead to improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects. For instance, AI algorithms are being used to predict the risk of cardiovascular disease based on patient-specific characteristics, enabling proactive interventions and preventative measures.
AI Implementation Challenges and Overcoming Them
Successful AI implementations often encounter challenges, including data quality issues, algorithmic bias, and the need for robust validation and regulatory approval. Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted approach. Robust data cleaning and standardization procedures are vital for ensuring the quality and reliability of AI algorithms. Researchers are actively working on methods to mitigate algorithmic bias, ensuring fair and equitable outcomes for all patient populations.
Rigorous validation studies and adherence to regulatory guidelines are critical for ensuring the safety and efficacy of AI-powered healthcare tools.
Key Insights from Case Studies
| Case Study | Impact | Challenges | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-powered diabetic retinopathy detection | Improved diagnostic accuracy and earlier detection, potentially reducing long-term complications | Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the AI model, dealing with potential bias in the training data | Careful data preparation and rigorous validation are crucial for reliable AI implementation in healthcare. Addressing potential biases in training data is paramount. |
| AI in drug discovery | Faster identification of potential drug candidates, reduced clinical trial costs and time | Integrating diverse data sources, ensuring data quality and accuracy, and navigating regulatory hurdles | Robust data management and a multi-disciplinary approach are vital for success in AI-driven drug discovery. |
| Personalized medicine using AI | Improved treatment outcomes, reduced side effects, and increased patient satisfaction | Data privacy and security concerns, ensuring the algorithm’s ability to generalize across diverse patient populations | Strong data governance and ethical considerations are critical in AI-driven personalized medicine. |
Final Summary
In conclusion, AI’s potential to transform healthcare is vast and multifaceted. While challenges remain, the benefits of AI-driven improvements in diagnostics, treatment, and patient care are undeniable. The future of healthcare likely rests on further integration of AI, fostering a more efficient, personalized, and accessible system for all.
Common Queries
What are the ethical concerns surrounding AI in healthcare?
Ethical concerns include potential bias in algorithms, data privacy and security, and the need for transparency and accountability in AI systems. Careful consideration and regulation are crucial to ensure equitable and responsible use of AI in healthcare.
How does AI impact the role of healthcare professionals?
AI is designed to augment, not replace, healthcare professionals. It automates tasks, provides valuable insights, and enhances diagnostic capabilities, allowing clinicians to focus on patient care and complex decision-making.
What are the major challenges in implementing AI in healthcare?
Challenges include data quality and availability, ensuring algorithm accuracy and reliability, regulatory hurdles, and the need for significant investment in infrastructure and training.
What are some examples of successful AI implementations in healthcare?
Several successful implementations exist, including AI-powered diagnostic tools for cancer detection, AI algorithms assisting in drug discovery, and AI systems aiding in personalized treatment plans. These examples showcase the tangible benefits and the potential of AI in healthcare.






